Dental X-rays
Adult X-rays
Today, dental radiography has become an indispensable tool for monitoring a patient's oral health.
It enables us to monitor the evolution of dental structure and anticipate problems (malformations, infections, pathologies, etc.). Thanks to a simple X-ray of the teeth, a dentist can detect abnormalities in good time and suggest appropriate treatment.
It is an essential complement to the clinical examination of the oral cavity before making a diagnosis. There are different types of X-ray.
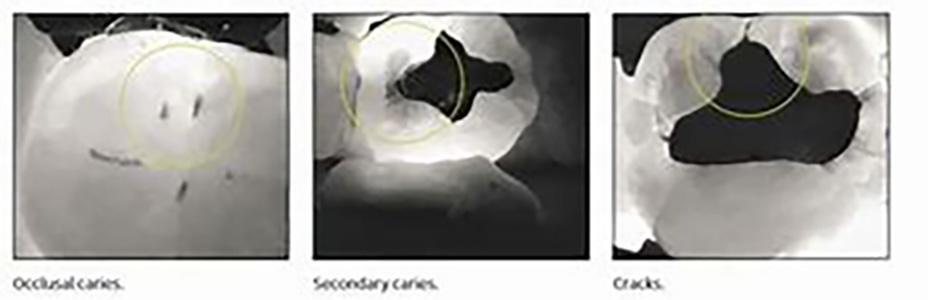
1 - Caries diagnosis with or without X-rays
Bite-wings
Retro-coronal radiography or bite-winging is very common and is often taken as a preventive measure, as it allows you to see any cavities between the teeth or below the gum line. The term bite-wing comes from the way patients have to bite the radiographic film.
Their use has been shown in the literature to be more effective than clinical examination in detecting proximal lesions in dentine, estimating lesion depth and monitoring lesion behavior.
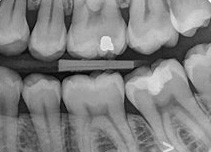
No X-rays? The Diagnocam
The new KaVo DIAGNOcam is the first camera to use tooth structure to diagnose caries. It uses transillumination (laser) with a wavelength of 780nm, which is used like a fiber optic.
A digital camera takes the image and transfers it directly to the computer screen. Caries lesions will appear on the image as dark areas. Images can be saved, making patient follow-up much simpler. This system guarantees a better understanding of caries diagnosis.
2 - Diagnosis of other oral problems
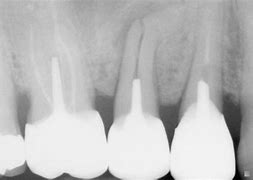
Periapical radiography
This type of dental X-ray captures an image of the entire tooth, including just beyond the root.
X-rays usually capture the entire row of upper or lower teeth in a single image. This type of X-ray can be used if your dentist suspects damage to the root tip of the tooth or a problem with the jawbone.
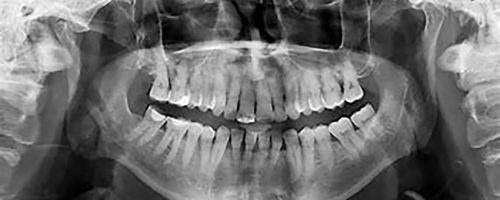
Panoramic radiography
Panoramic radiography uses a special device that takes an image of all your upper and lower teeth. The result is a 2-D image of your mouth in 3-D.
More precise and complete than a clinical dental examination, an orthopantomogram can reveal tooth or gum lesions that are invisible or barely visible to the naked eye, such as incipient decay, cysts, tumors or abscesses.
The dental panoramic also highlights any abnormalities in wisdom teeth or impacted teeth.
Dental X-rays are also used to determine the position and evolution of teeth, particularly in children. It can also be used to monitor bone loss and gum condition.
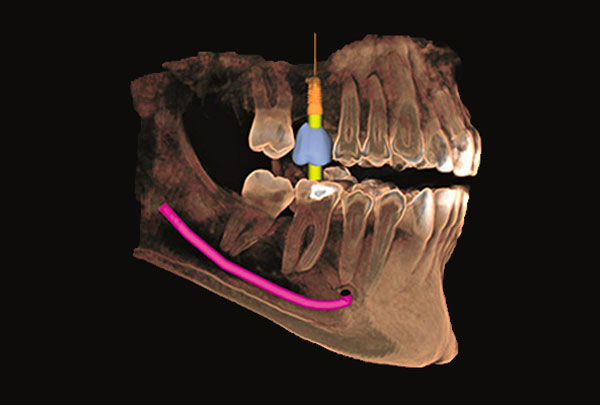
3D Cone Beam
CBCT or "cone beam" X-rays are an imaging method that uses computerized technology to convert two-dimensional images into a three-dimensional (3D) image.
Compared to a traditional two-dimensional dental X-ray, which shows a flat image, the 3D image shows all dimensions and aspects of the teeth and surrounding bone.
For the patient, this means a precise diagnosis of an area of concern that would not have been possible without this technology. What's more, for patients who have chosen to replace missing teeth, the dentist can examine, diagnose and virtually place a dental implant in your mouth on the computer in front of you before treatment begins.
This advanced, more precise approach using Cone Beam imaging means fewer complications, less invasive therapy, faster healing times and, ultimately, better patient outcomes.
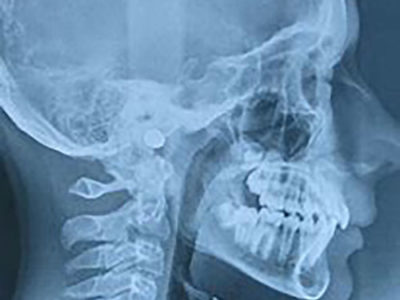
3 - Orthodontic diagnosis
Profile teleradiography
Teleradiography is a radiological imaging technique that can be performed from the front and the side, allowing visualization of the entire skull. This examination, in addition to the dental panoramic, enables the orthodontist to identify various points of interest and measures necessary for certain orthodontic treatments.